Background
In 2015, CERT published a blog post called The Risks of SSL Inpsection, which outlined the potential weaknesses introduced by deploying an SSL inspection solution. Earlier this year, US-CERT published an alert called TA17-075A HTTPS Interception Weakens TLS Security, which suggested comparing a directly-connected browser against the same browser behind a product that performs HTTPS inspection.
The Test
Given the ease of availability of the Untangle NG Firewall, I used their SSL Inspector as an example. By default the Untangle SSL Inspector did not inspect traffic to https://badssl.com. As a result, I modified the default configuration of the SSL Inspector to inspect all HTTPS traffic. The platform used for the test was Windows 7 with both Firefox 54.0.1 and Chrome 60.
Legend
Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Green | Unsafe connection blocked, and proper reason given. |
| Yellow | Unsafe connection blocked, without proper reason. |
| Red | Unsafe connection allowed. |
| White | Connection allowed. Security impact unclear. |
Test Results
Firefox 54.0.1 (Windows) | Chrome 60 (Windows) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate | |||
| expired | SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE | NET::ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID | Reset |
| wrong.host | SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERT_DOMAIN | NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID | Certificate validation left up to client |
| self-signed | SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER | NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID | Reset |
| untrusted-root | SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER | NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID | Reset |
| revoked | SEC_ERROR_REVOKED_CERTIFICATE | NET::ERR_CERT_REVOKED | Allowed |
| pinning-test | MOZILLA_PKIX_ERROR_KEY_PINNING_FAILURE | NET::ERR_SSL_PINNED_KEY_NOT_IN_CERT_CHAIN | Allowed |
| no-common-name | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| no-subject | Allowed | Allowed | Reset |
| incomplete-chain | Allowed | Allowed | Reset |
| sha1-intermediate | SEC_ERROR_CERT_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM_DISABLED | Allowed | Allowed |
| sha256 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| sha384 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| sha512 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | |
| 10000-sans | SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HANDSHAKE | ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR | Certificate validation left up to client |
| Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | |
| ecc384 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| rsa2048 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| rsa8192 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| Cipher Suite | |||
| cbc | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| rc4-md5 | SSL_ERROR_NO_CYPHER_OVERLAP | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| rc4 | SSL_ERROR_NO_CYPHER_OVERLAP | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| 3des | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| null | SSL_ERROR_NO_CYPHER_OVERLAP | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| mozilla-old | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| mozilla-intermediate | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| mozilla-modern | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| Key exchange | |||
| dh480 | SSL_ERROR_WEAK_SERVER_EPHEMERAL_DH_KEY | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| dh512 | SSL_ERROR_WEAK_SERVER_EPHEMERAL_DH_KEY | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| dh1024 | Allowed | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Allowed |
| dh2048 | Allowed | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Allowed |
| dh-small-subgroup | Allowed | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Allowed |
| dh-composite | Allowed | ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH | Reset |
| static-rsa | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| Certificate Transparency | |||
| invalid-expected-sct | Allowed | NET::ERR_CERTIFICATE_TRANSPARENCY_REQUIRED | Allowed |
| Defunct | |||
| sha1-2016 | SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE | NET::ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM | Reset |
| sha1-2017 | SEC_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERTIFICATE | NET::ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM | Reset |
About the red "Allowed" items above
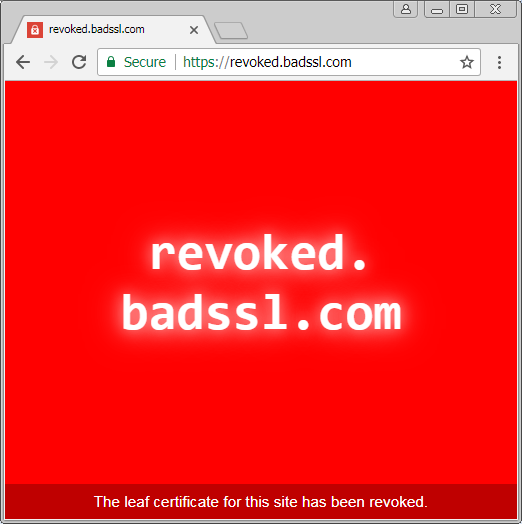
Any of the red "Allowed" items in the table above are indicators that a connection is allowed, while a secure browser configuration will not allow it. Let's consider the case where a certificate for a website is revoked. First, let's visit such a site with Chrome and a direct internet connection:
Chrome doesn't allow the connection to a website with a revoked HTTPS certificate. The reasoning here is that certificates are revoked for a reason: they are no longer safe to use. An example reason for a certificate being revoked is when a private key is leaked to the public. At this point, communications between the server and the client will no longer be secure, as an attacker with the private key may be able to decrypt the communications. Now let's try the same connection when the client system has its internet connection provided by Untangle SSL Inspector:
Whoops! With SSL inspection enabled for all traffic, Untangle allows clients to connect to sites that have had their certificates revoked.
About the yellow "Reset" items above
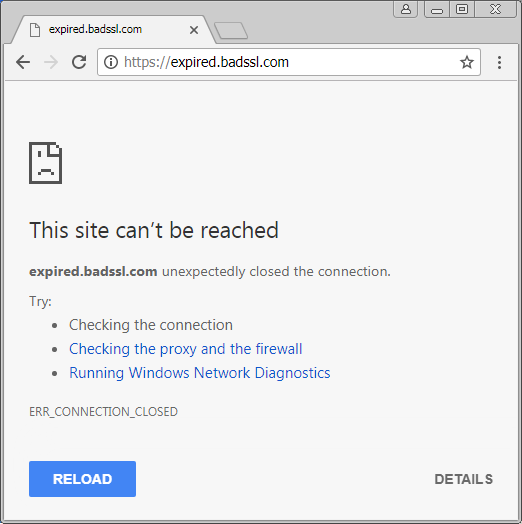
When a connection is insecure, the client browser will often display reasons for why this is the case. For example, the following is what the user sees if Chrome is used with a direct internet connection to visit a website that provides an expired certificate:
While the technical details of what NET::ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID may be outside the grasp of many users, the friendly description of the consequences of proceeding with the connection are clearly explained. That is, an attacker may be able to steal passwords, messages, or credit cards. Let's proceed attempting to make the same connection through the Untangle SSL Inspection product:
Here, the browser recommends that the user verify their internet connection and firewall, and run Windows Network Diagnostics. None of which will actually address the problem.
Conclusion
As first mentioned in the 2015 blog post The Risks of SSL Inspection, the ability to inspect HTTPS traffic does not come without its costs. Given the ease of testing the impact with the badssl.com website, this impact is now easier for users and network administrators to determine. The table above currently only contains results for the Untangle SSL Inspector product, however other similar products have similar results. HTTPS inspection is not something that can be done at the network level without negatively affecting the security of the clients.
HTTPS inspection aims to improve network security, but it does so at the cost of client security. In many cases, this is a reasonable trade-off for an organization to make. Just be sure that it is a conscious and well-informed decision.